- how-to 15
- generative-models 12
- nlp 7
- rl 7
- cv 6
- diffusion 6
- latex 6
- text2image 5
- detection 4
- sampling 4
- pytorch 3
- tensorflow 3
- llm 3
- optimization 2
- metrics 2
- transformer 2
- attention 2
- visualisation 2
- augmentation 1
- vae 1
- normalization 1
- algorithms 1
- auto-regressive 1
- speech 1
- segmentation 1
- quantum 1
- super-resolution 1
how-to
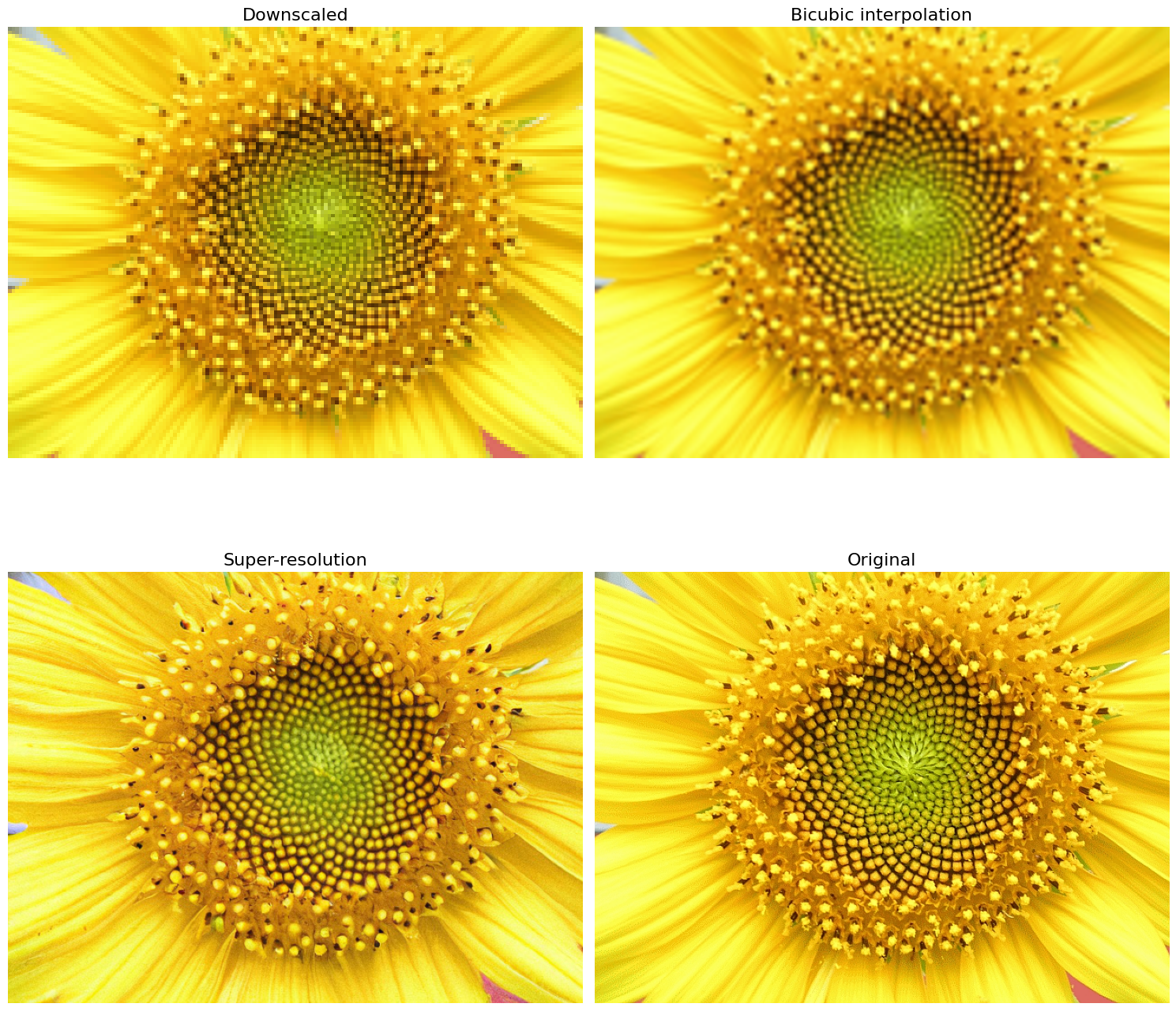
A quick introduction to super-resolution using Stable Diffusion and the Diffusers library
In this blog post, we will show how to use the diffusers library to upscale images using the Stable Diffusion Upscaler model. The model is a diffusion-based super-resolution model that is capable of generating high-quality upscaled images.

How to create matrices in LaTeX
This blog post will guide you through the steps of creating matrices in LaTeX. It will start with the general syntax and then explain how to create row and column vectors, determinants, arbitrary sized matrices and nested matrices. It will conclude with several examples of real world matrices and the use of matrices in mathematical expressions.

How to Create Quantum Gate Diagrams in Python
A key concept in quantum computing is the quantum logic gate. Quantum gates are the building blocks of quantum circuits. In this blog we will learn how to create quantum gate and quantum circuit diagrams in Python using the SymPy library.

How I ran the Hugging Face Diffusers Textual Inversion example on an AWS EC2 Instance
This blog extends the Hugging Face Diffusers Textual Inversion tutorial by outlining the steps I took to set up an AWS EC2 instance, install libraries and run the example.

A Minimalist ChatGPT for Jupyter Notebook or Command Line
In this blog post, we will explore how to implement a minimalist ChatGPT-style app in a Jupyter Notebook. The goal is to provide an understanding of the important concepts, components, and techniques required to create a chat app on top of a large language model (LLM), specifically OpenAI’s GPT.

How to use curly brackets {} in LaTeX
In this tutorial, we will discuss various ways to use curly brackets $\{\}$ in LaTeX. The simplest case involves using curly brackets to denote a set. However, curly brackets, or braces, can also be used to group multiple lines of calculations and mathematical equations or to add explanatory text above or below the expressions.

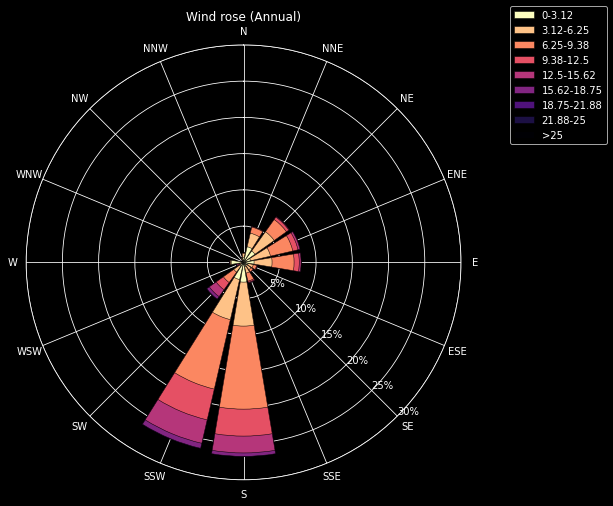
How to plot a Windrose in Python
A windrose is a circular histogram that shows the distribution of wind speeds and directions over a period of time. In this tutorial we will learn how to plot a windrose in Python using Matplotlib and Plotly.
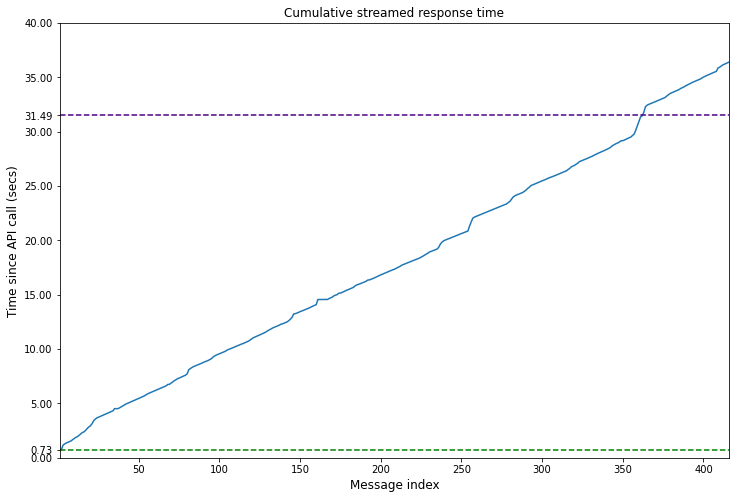
How to stream ChatGPT responses from the OpenAI API
In this blog post we will learn how you can replicate this experience of the ChatGPT web application by streaming responses from the OpenAI API.
Animations in Plotly.js
In this blog, we will demystify the process of creating interactive animations using Plotly.js.
Writing Sums, Products and Integrals in LaTeX
In this blog post, we will learn how to write sums, products, and various types of integrals using LaTeX.

Representing Norms in LaTeX
In this blog post, we will learn how to write the norm function in LaTeX and how to represent different types of norms.

Writing Ceil, Floor and Abs in LaTeX
In this blog post, we will learn how to write the ceiling, floor and absolute value functions in LaTeX, both in mathematical notation and as text.

Simplifying LaTeX Notation with \newcommand
In this blog post, we’ll explore how to define convenient shortcuts using \newcommand in LaTeX, making your notation more concise and readable.

How to create non-square images with DALL-E 2
The DALL-E API from OpenAI is a very powerful image generation tool. However one limitation is that it only outputs square images. In this tutorial we will learn how to generate images of arbitrary dimension such as portraits and landscapes.

How to generate subtitles with the Whisper API in Python
In this tutorial we will learn how to use the Whisper API to generate subtitles for a video. We will generate subtitles for the opening of A Star Is Born (1937), an early colour movie that has been frequently remade.

generative-models
A quick introduction to super-resolution using Stable Diffusion and the Diffusers library
In this blog post, we will show how to use the diffusers library to upscale images using the Stable Diffusion Upscaler model. The model is a diffusion-based super-resolution model that is capable of generating high-quality upscaled images.

How I ran the Hugging Face Diffusers Textual Inversion example on an AWS EC2 Instance
This blog extends the Hugging Face Diffusers Textual Inversion tutorial by outlining the steps I took to set up an AWS EC2 instance, install libraries and run the example.

A Minimalist ChatGPT for Jupyter Notebook or Command Line
In this blog post, we will explore how to implement a minimalist ChatGPT-style app in a Jupyter Notebook. The goal is to provide an understanding of the important concepts, components, and techniques required to create a chat app on top of a large language model (LLM), specifically OpenAI’s GPT.

How to stream ChatGPT responses from the OpenAI API
In this blog post we will learn how you can replicate this experience of the ChatGPT web application by streaming responses from the OpenAI API.

How to create non-square images with DALL-E 2
The DALL-E API from OpenAI is a very powerful image generation tool. However one limitation is that it only outputs square images. In this tutorial we will learn how to generate images of arbitrary dimension such as portraits and landscapes.

PixelCNN
The PixelRNN family of auto-regressive architectures consists of models that learn to generate images a pixel at a time. In this post we will focus on the PixelCNN model which is based on the same principles but uses convolutional layers instead of recurrent layers. It is simpler to implement and once we have grasped the core concepts, it is straightforward to understand the recurrent versions.
Implementing the Fréchet Inception distance
A popular metric for evaluating image generation models is the Fréchet Inception Distance (FID). Like the Inception score, it is computed on the embeddings from an Inception model. But unlike the Inception score, it makes use of the true images as well as the generated ones. In the post we will learn how to implement it in PyTorch.

Speeding Up Diffusion Sampling
An important disadvantage with diffusion models is that a large number forward passes - typically 1000 or more - are needed to generate samples, making inference slow and expensive. In this post we will look at a couple of different methods that have been developed to speed up inference.
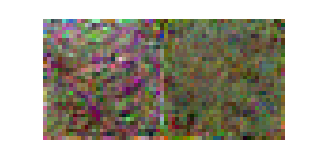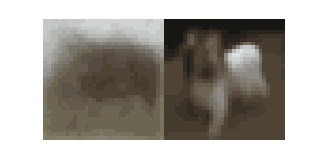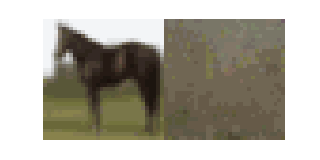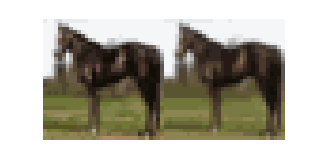
An Introduction to Diffusion
In this blog we will learn about the basic diffusion-based generative model introduced in Denoising Diffusion Probabilistic Models (DDPM). This post will cover the basics at a relatively high level but along the way there will be optional exercises that will help you to delve deeper into the mathematical details.

A quick overview of GLIDE
You have probably come across DALL-E 2 a large-scale image generation model from OpenAI. If not, you can read about it in their blog. DALL-E 2 uses a class of models known as diffusion models. The DALL-E 2 paper does not go into a lot of detail about the model architecture since it mostly extends an earlier architecture GLIDE. This article provides a brief introduction to the GLIDE architecture.

Variational Auto-Encoder - Part 2 / Implementing a simple model
Introduction
In the previous post we motivated the idea of a Variational Auto Encoder. Here we will have a go at implementing a very simple model to get a sense of all the components steps involved.
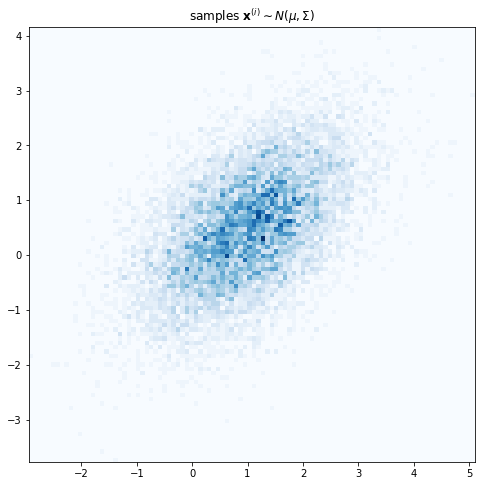
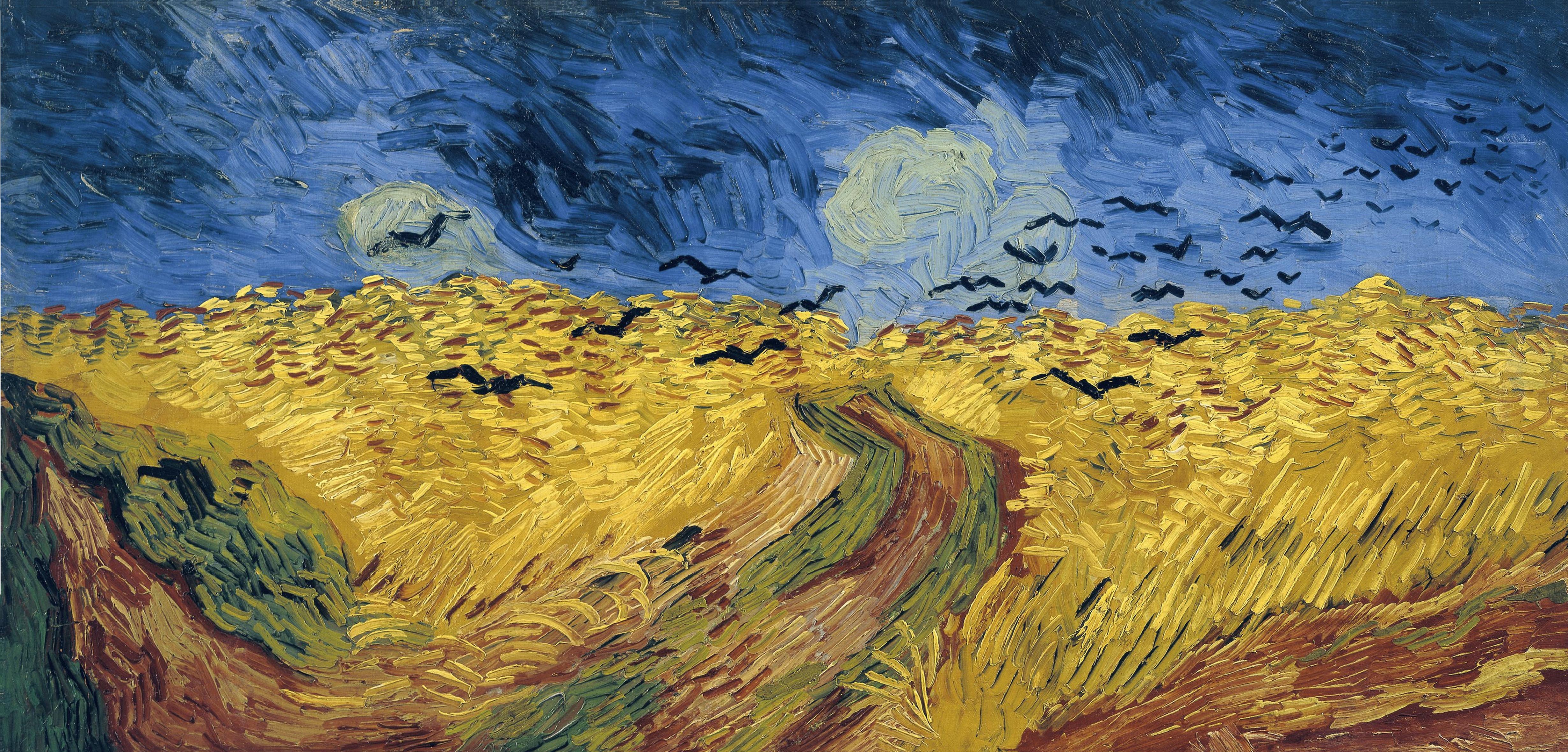
Variational Auto-Encoder - Part 1 / Introduction
Consider this painting by Vincent Van Gogh known as “Wheatfield with Crows”. Suppose you want to learn a probability distribution over Van Gogh’s paintings. What the computer or a deep learning algorithm sees when it looks at this painting is a grid of RGB pixel intensities. So one approach might be to model the data as a sequence of individual pixels. Yet that is manifestly not how the artist has constructed the painting.

nlp
A Minimalist ChatGPT for Jupyter Notebook or Command Line
In this blog post, we will explore how to implement a minimalist ChatGPT-style app in a Jupyter Notebook. The goal is to provide an understanding of the important concepts, components, and techniques required to create a chat app on top of a large language model (LLM), specifically OpenAI’s GPT.

How to stream ChatGPT responses from the OpenAI API
In this blog post we will learn how you can replicate this experience of the ChatGPT web application by streaming responses from the OpenAI API.

How to generate subtitles with the Whisper API in Python
In this tutorial we will learn how to use the Whisper API to generate subtitles for a video. We will generate subtitles for the opening of A Star Is Born (1937), an early colour movie that has been frequently remade.

Transformer Part 2: Train a Translation Model
In Part 1 of the tutorial we learned how to how build a transformer model. Now it is time to put it into action. There are lots of things we can do with a transformer but we will start off with a machine translation task to translate from Spanish to English.

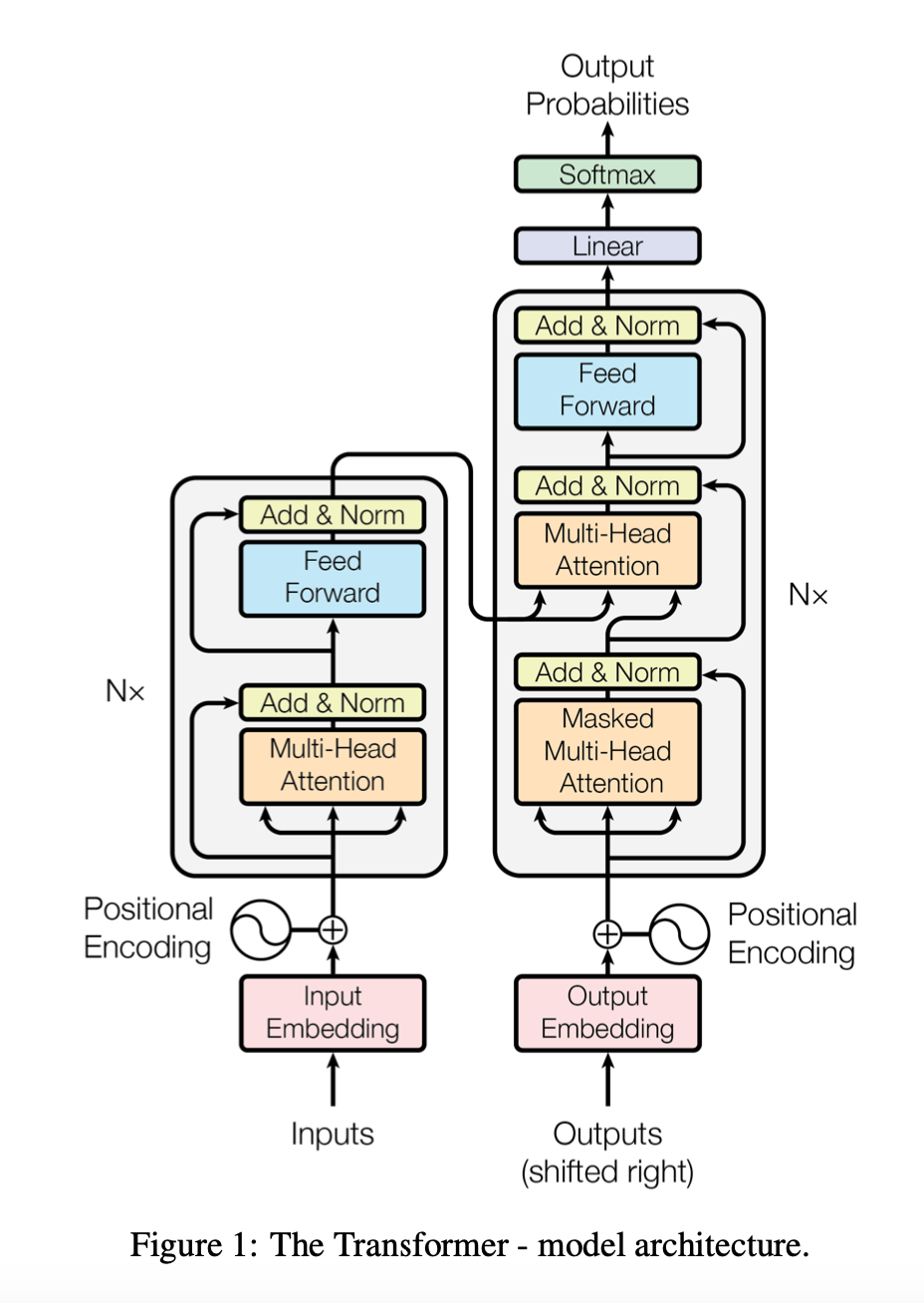
Transformer Part 1: Build
Since its introduction the Transformer architecture has become very influential and has had successes in many tasks not just in NLP but in other areas like vision. This tutorial is inspired by the approach in The Annotated Transformer and uses text directly quoted from the paper to explain the code.
Veg2vec - word embeddings for plant-based foods with health benefits
One of the most exciting uses of machine learning is scientific discovery. Sometimes long before a discovery is officially made people have written about similar ideas and one could speculate what might have happened if some dots had been connected sooner. This is exactly what the mat2vec model (code, paper) seeks to do with the help of AI

Padding in PyTorch and TensorFlow embedding layers
When batching inputs for sequence models you often have sequences of variable sizes and you need to pad some of the inputs so that you can input them as a single tensor. For example here is a pair of lines in a dialogue from Twelfth Night Act 2, Scene 4 which are of variable length as represented here

However you don’t want the pad locations to influence the weight updates. In this post we will learn how PyTorch and TensorFlow approach this via their respective embedding layers.
rl
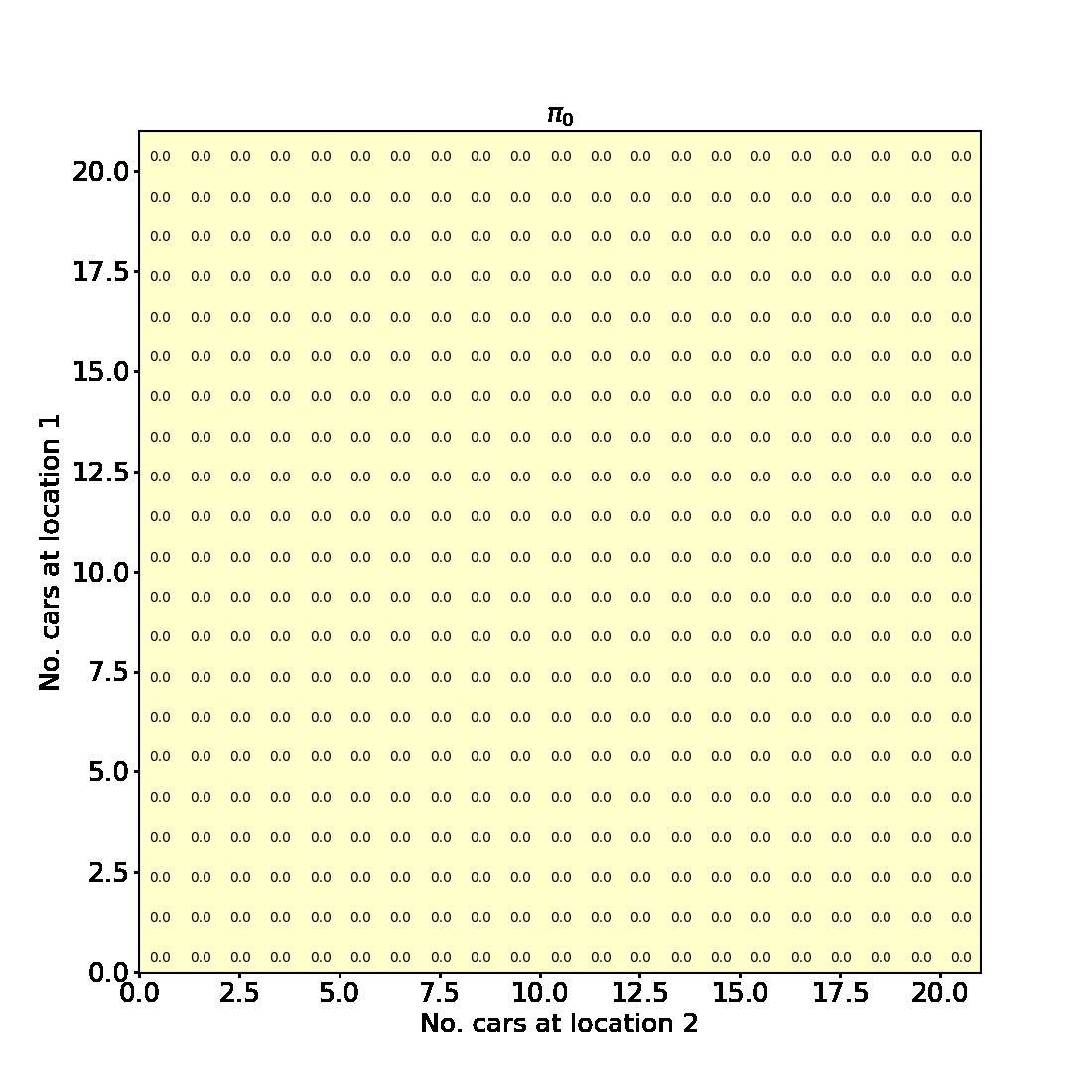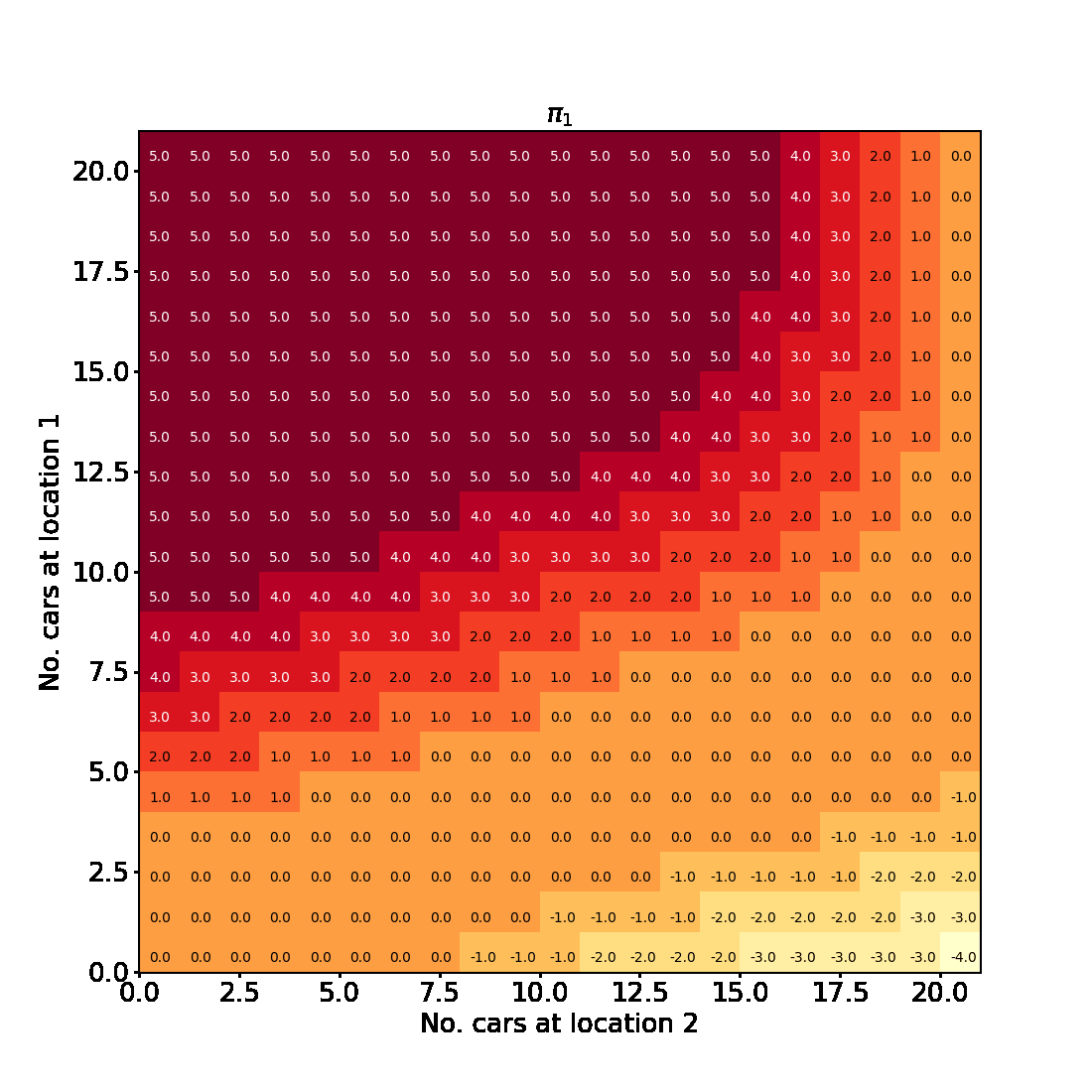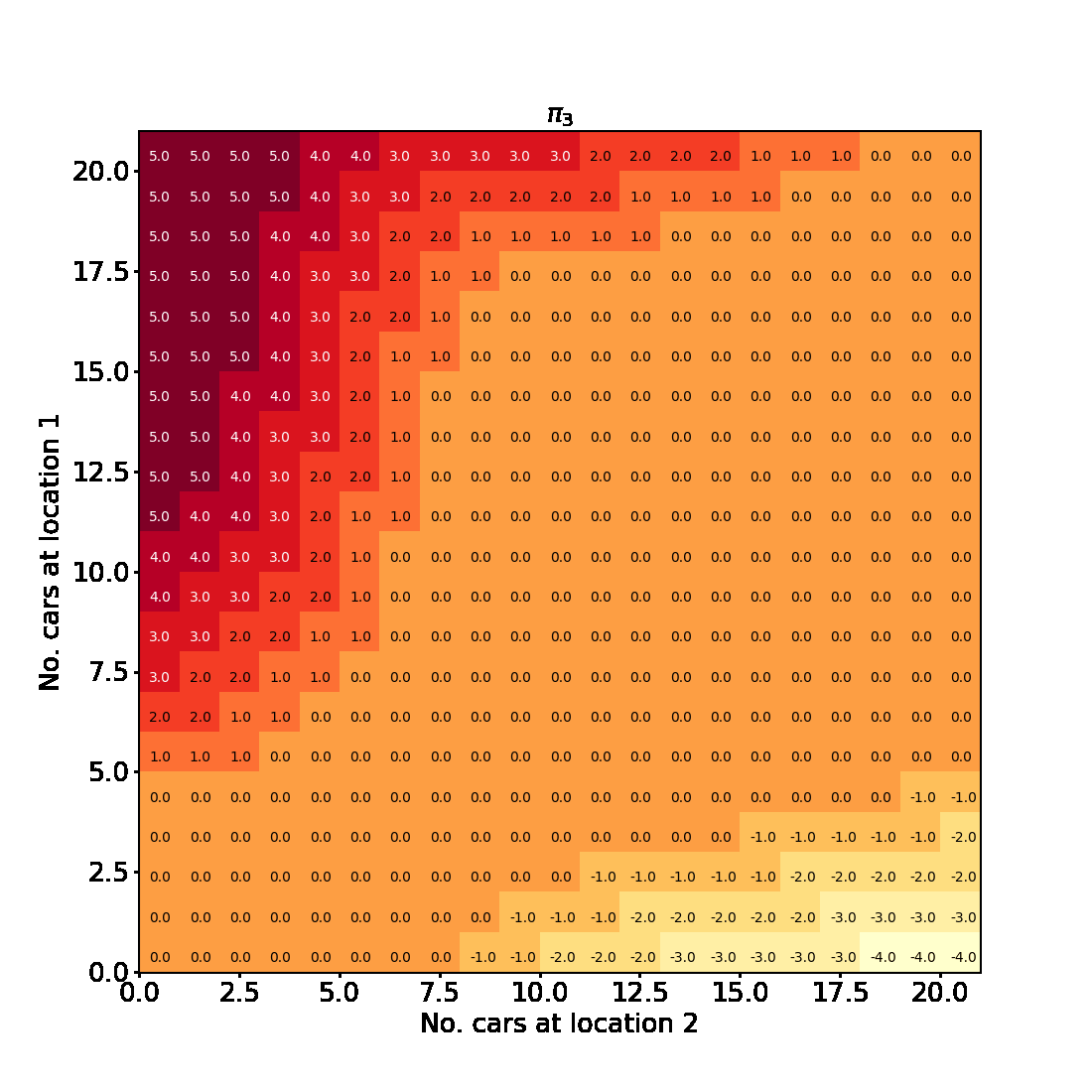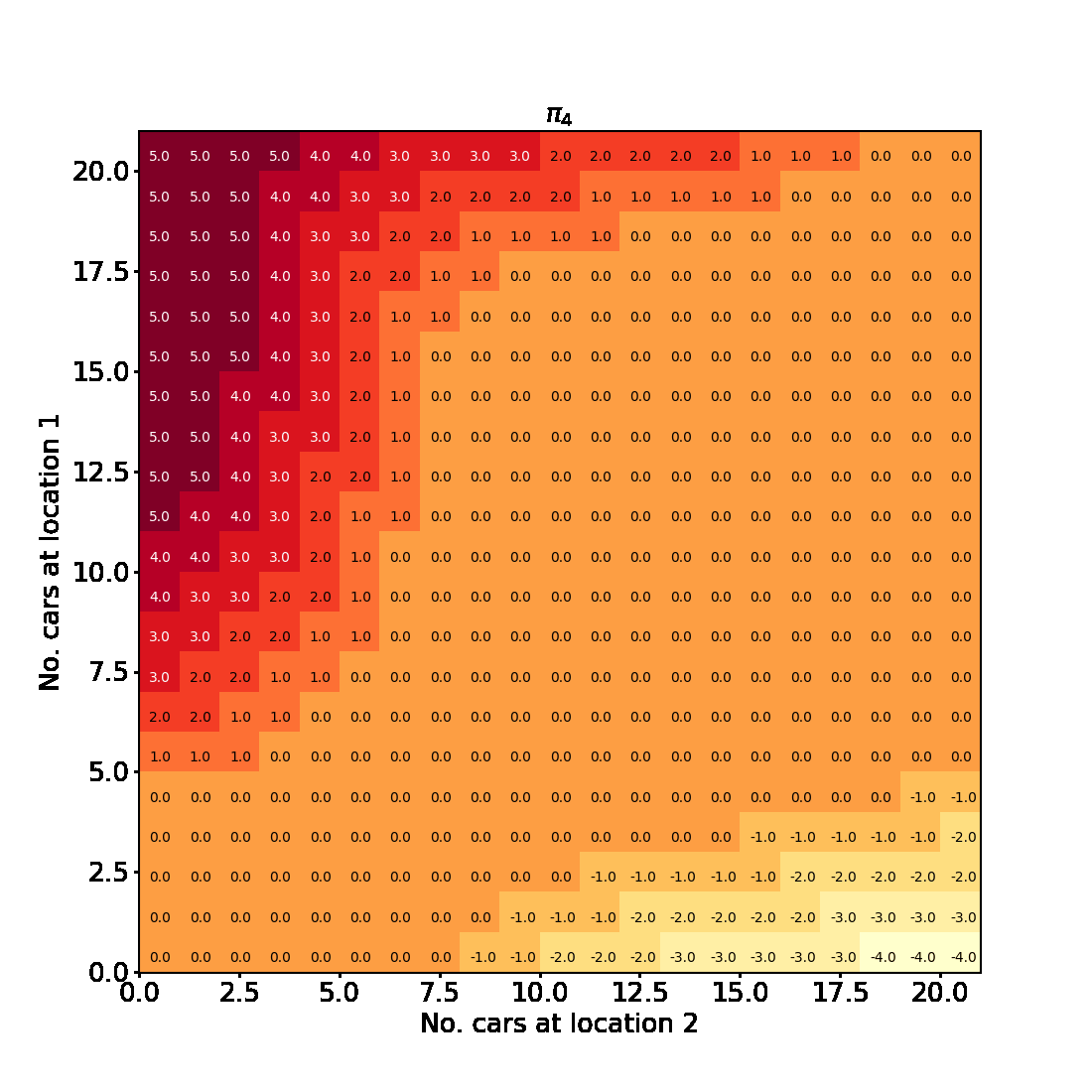
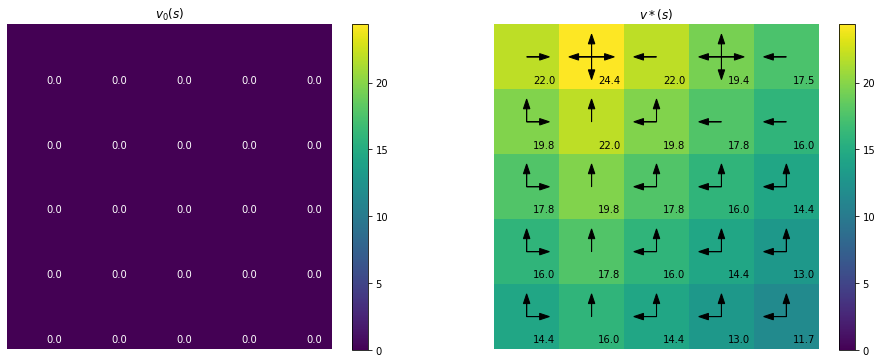
Policy Iteration for finite MDPs
In this blogpost we will implement Example 4.2 from Chapter 4 Reinforcement Learning (Sutton and Barto aka the RL book). This is an example of a problem involving a finite Markov Decision Process for which policy iteration is used to find an optimal policy.
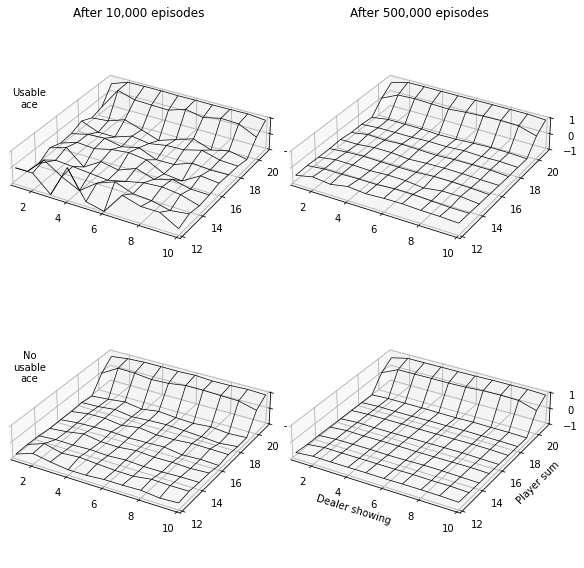
First Visit Monte Carlo Prediction for Blackjack (RL S&B Example 5.1)
In this tutorial we will demonstrate how to implement Example 5.1: Blackjack from Reinforcement Learning (Sutton and Barto).
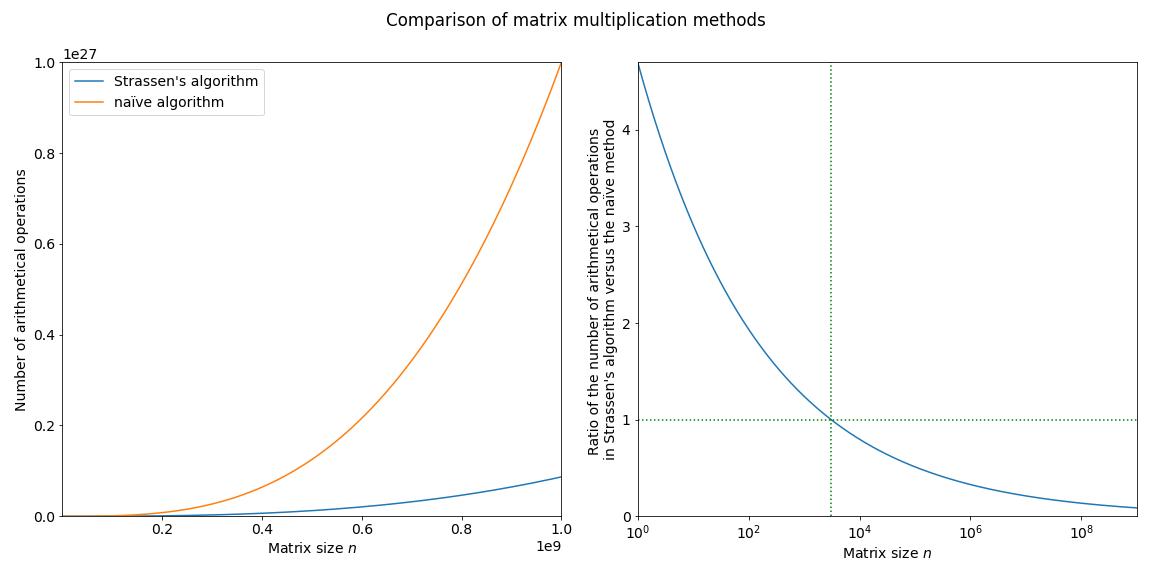
Strassen’s algorithm for matrix multiplication
This is the first of a planned series of blogs covering background topics for DeepMind’s AlphaTensor paper. In this post we will cover Strassen’s algorithm for matrix multiplication.
REINFORCE on the short-corridor gridworld, Part 2 (RL S&B Chapter 13)
In the previous post we introducted the short-corridor gridworld with switched actions. We found an analytical solution for the probability for moving right. Now we will use the REINFORCE algorithm to solve this problem.
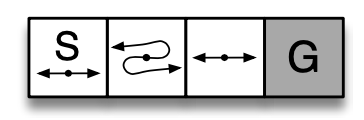
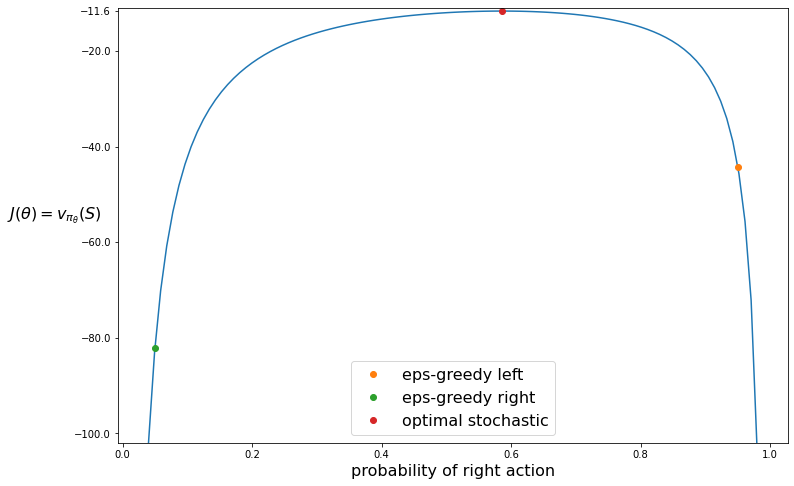
REINFORCE on the short-corridor gridworld, Part 1 (RL S&B Chapter 13)
In this tutorial we will demonstrate how to implement Example 13.1 of Reinforcement Learning (Sutton and Barto).
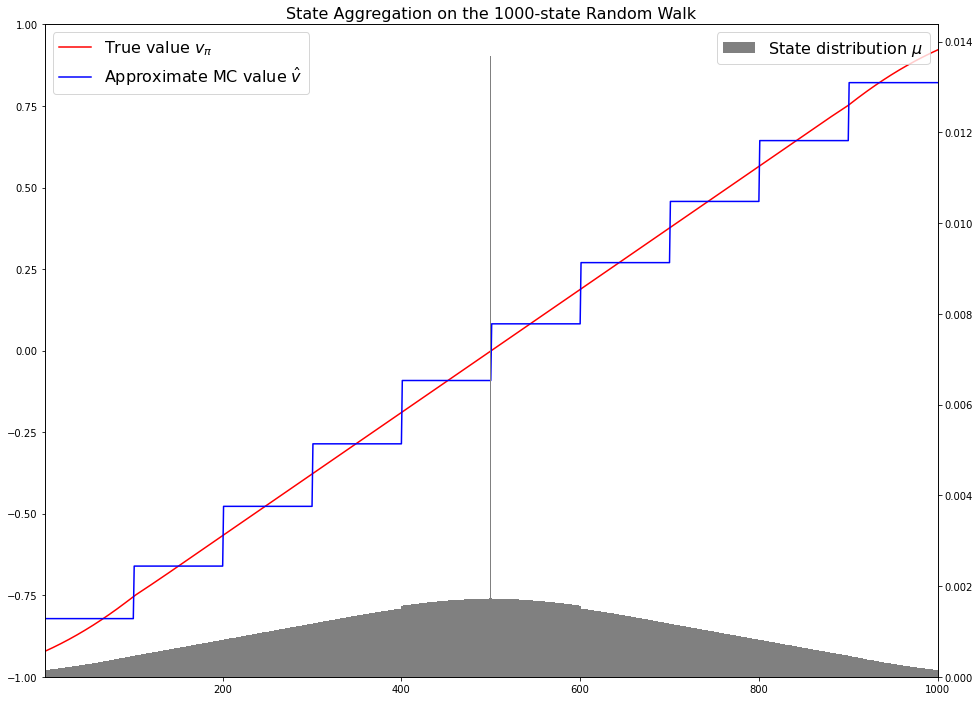
Gradient Monte Carlo for Value Function Approximation (RL S&B Example 9.1)
In this post we will implement Example 9.1 from Chapter 9 Reinforcement Learning (Sutton and Barto). This is an example of on-policy prediction with approximation which means that you try to approximate the value function for the policy you are following right now. We will be using Gradient Monte Carlo for approximating $v_\pi(s)$
Vectorising the Bellman equations (RL S&B Examples 3.5, 3.8)
In this blog post we will reproduce Examples 3.5 and 3.8 in Reinforcement Learning (Sutton and Barto) involving the Bellman equation. This post presumes a basic understanding of reinforcement learning in particular policy and value and will just outline the theory that is needed in order to implement the examples.
cv
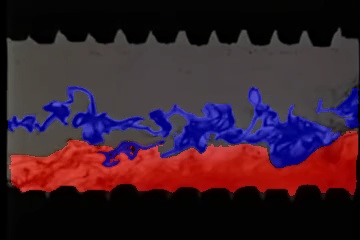
Turbulent flow segmentation with SAM
A simple example demonstrating the use of Meta’s Segment Anything Model (SAM) on a video of turbulent fluid flow.
Generating crops from images
This post explains how to implement a function to generate a crop of a particular object from an image given the position of the centroid of the object. The images below show an example use case: cropping all the individual oranges from an image.

Non-maximum suppression (NMS)
This blogpost contains a quick practical introduction to a popular post-processing clustering algorithm used in object detection models. The code used to generate the figures and the demo can be found in this Colab notebook.
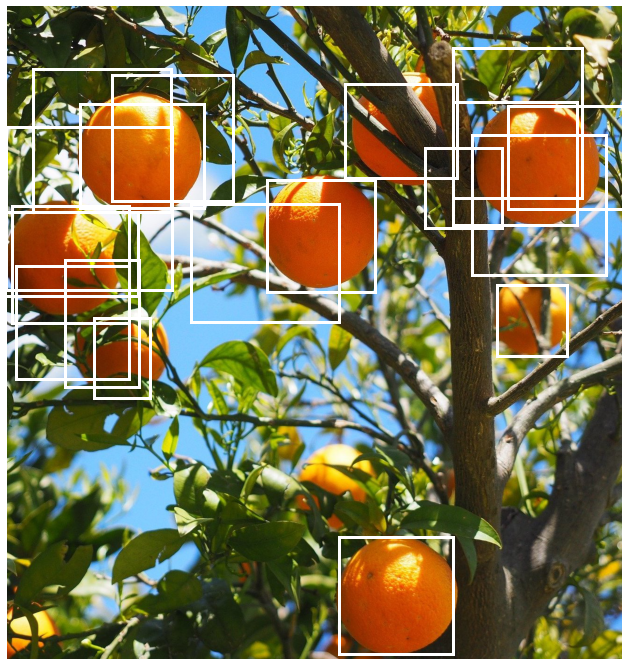
Vectorizing Intersection over Union (IoU)
Supporting batched data is an important requirement for a deep learning pipeline to enable time efficient model training. Often when writing a function, the easiest way to start is to first handle one element and then use a for loop over all the elements in the batch.
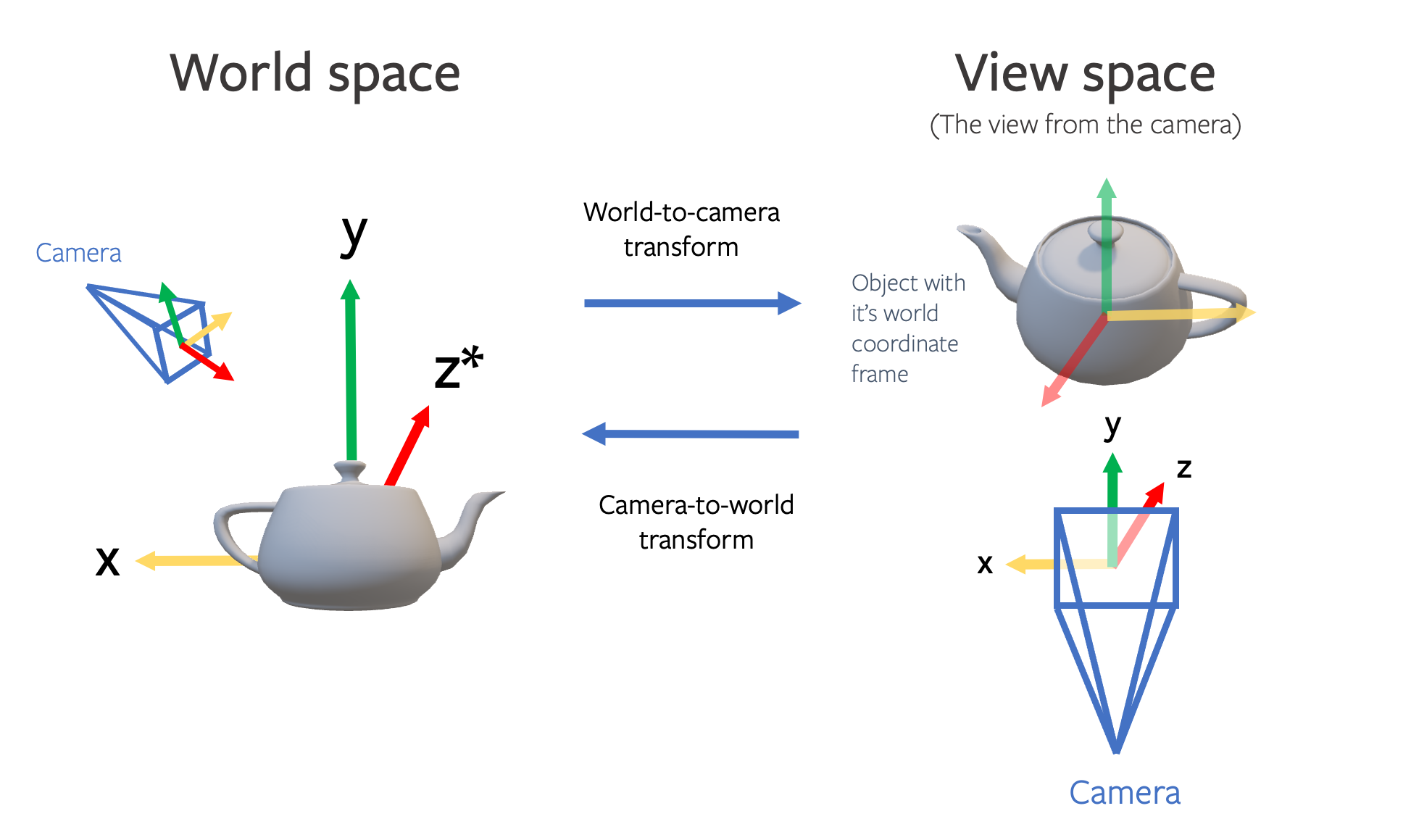
Converting Camera Conventions
When working with computer vision models we frequently need to know information about the camera that was used to generate the image. This includes information about the position of the camera in the world coordinate system as well as the intrinsic properties of the camera such as the focal length.
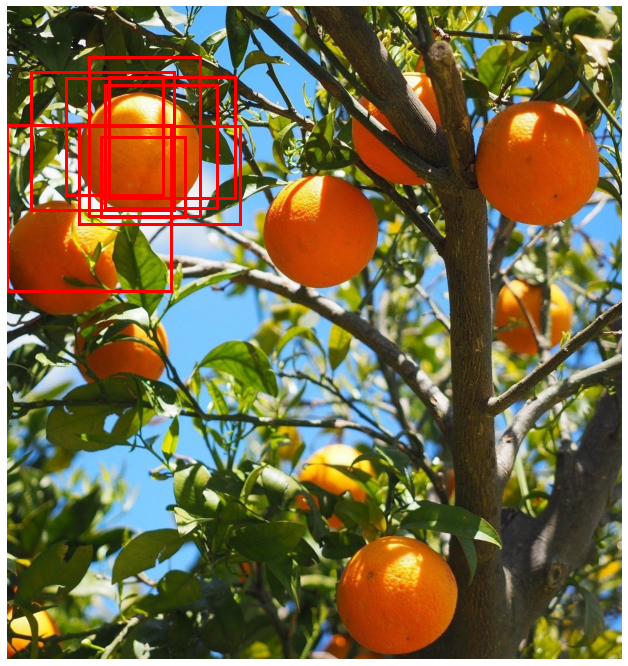
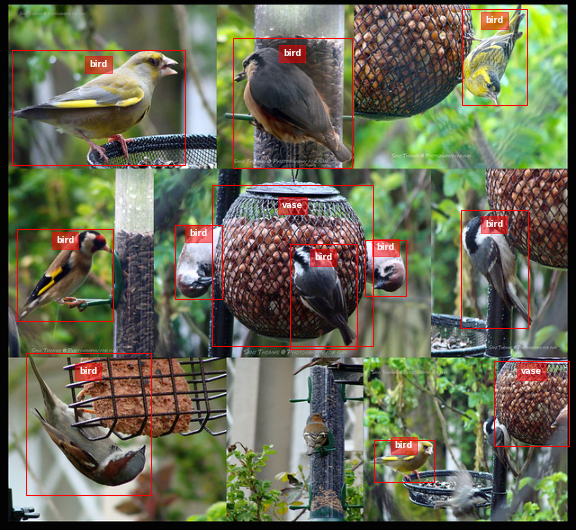
Plotting bounding boxes for object detection
When working with detection models in a pipeline you often need to visualize the bounding boxes to sanity check the predictions. Bounding boxes can be defined in different ways so this is also useful to confirm the convention being used.

diffusion
A quick introduction to super-resolution using Stable Diffusion and the Diffusers library
In this blog post, we will show how to use the diffusers library to upscale images using the Stable Diffusion Upscaler model. The model is a diffusion-based super-resolution model that is capable of generating high-quality upscaled images.

How I ran the Hugging Face Diffusers Textual Inversion example on an AWS EC2 Instance
This blog extends the Hugging Face Diffusers Textual Inversion tutorial by outlining the steps I took to set up an AWS EC2 instance, install libraries and run the example.

How to create non-square images with DALL-E 2
The DALL-E API from OpenAI is a very powerful image generation tool. However one limitation is that it only outputs square images. In this tutorial we will learn how to generate images of arbitrary dimension such as portraits and landscapes.

Speeding Up Diffusion Sampling
An important disadvantage with diffusion models is that a large number forward passes - typically 1000 or more - are needed to generate samples, making inference slow and expensive. In this post we will look at a couple of different methods that have been developed to speed up inference.

An Introduction to Diffusion
In this blog we will learn about the basic diffusion-based generative model introduced in Denoising Diffusion Probabilistic Models (DDPM). This post will cover the basics at a relatively high level but along the way there will be optional exercises that will help you to delve deeper into the mathematical details.

A quick overview of GLIDE
You have probably come across DALL-E 2 a large-scale image generation model from OpenAI. If not, you can read about it in their blog. DALL-E 2 uses a class of models known as diffusion models. The DALL-E 2 paper does not go into a lot of detail about the model architecture since it mostly extends an earlier architecture GLIDE. This article provides a brief introduction to the GLIDE architecture.

latex
How to create matrices in LaTeX
This blog post will guide you through the steps of creating matrices in LaTeX. It will start with the general syntax and then explain how to create row and column vectors, determinants, arbitrary sized matrices and nested matrices. It will conclude with several examples of real world matrices and the use of matrices in mathematical expressions.

How to use curly brackets {} in LaTeX
In this tutorial, we will discuss various ways to use curly brackets $\{\}$ in LaTeX. The simplest case involves using curly brackets to denote a set. However, curly brackets, or braces, can also be used to group multiple lines of calculations and mathematical equations or to add explanatory text above or below the expressions.

Writing Sums, Products and Integrals in LaTeX
In this blog post, we will learn how to write sums, products, and various types of integrals using LaTeX.

Representing Norms in LaTeX
In this blog post, we will learn how to write the norm function in LaTeX and how to represent different types of norms.

Writing Ceil, Floor and Abs in LaTeX
In this blog post, we will learn how to write the ceiling, floor and absolute value functions in LaTeX, both in mathematical notation and as text.

Simplifying LaTeX Notation with \newcommand
In this blog post, we’ll explore how to define convenient shortcuts using \newcommand in LaTeX, making your notation more concise and readable.

text2image
A quick introduction to super-resolution using Stable Diffusion and the Diffusers library
In this blog post, we will show how to use the diffusers library to upscale images using the Stable Diffusion Upscaler model. The model is a diffusion-based super-resolution model that is capable of generating high-quality upscaled images.

How I ran the Hugging Face Diffusers Textual Inversion example on an AWS EC2 Instance
This blog extends the Hugging Face Diffusers Textual Inversion tutorial by outlining the steps I took to set up an AWS EC2 instance, install libraries and run the example.

Speeding Up Diffusion Sampling
An important disadvantage with diffusion models is that a large number forward passes - typically 1000 or more - are needed to generate samples, making inference slow and expensive. In this post we will look at a couple of different methods that have been developed to speed up inference.

An Introduction to Diffusion
In this blog we will learn about the basic diffusion-based generative model introduced in Denoising Diffusion Probabilistic Models (DDPM). This post will cover the basics at a relatively high level but along the way there will be optional exercises that will help you to delve deeper into the mathematical details.

A quick overview of GLIDE
You have probably come across DALL-E 2 a large-scale image generation model from OpenAI. If not, you can read about it in their blog. DALL-E 2 uses a class of models known as diffusion models. The DALL-E 2 paper does not go into a lot of detail about the model architecture since it mostly extends an earlier architecture GLIDE. This article provides a brief introduction to the GLIDE architecture.

detection
Generating crops from images
This post explains how to implement a function to generate a crop of a particular object from an image given the position of the centroid of the object. The images below show an example use case: cropping all the individual oranges from an image.

Non-maximum suppression (NMS)
This blogpost contains a quick practical introduction to a popular post-processing clustering algorithm used in object detection models. The code used to generate the figures and the demo can be found in this Colab notebook.

Vectorizing Intersection over Union (IoU)
Supporting batched data is an important requirement for a deep learning pipeline to enable time efficient model training. Often when writing a function, the easiest way to start is to first handle one element and then use a for loop over all the elements in the batch.

Plotting bounding boxes for object detection
When working with detection models in a pipeline you often need to visualize the bounding boxes to sanity check the predictions. Bounding boxes can be defined in different ways so this is also useful to confirm the convention being used.

sampling
Speeding Up Diffusion Sampling
An important disadvantage with diffusion models is that a large number forward passes - typically 1000 or more - are needed to generate samples, making inference slow and expensive. In this post we will look at a couple of different methods that have been developed to speed up inference.

Spherical Interpolation
\(\newcommand{\vv}{\mathbf{v}}\) In machine learning applications you sometimes want to interpolate vectors in a normalised latent space such as when interpolating between two images in a generative model. An appropriate method for doing this is spherical interpolation. In this post we will derive the formula for this method and show how it differs from linear interpolation.
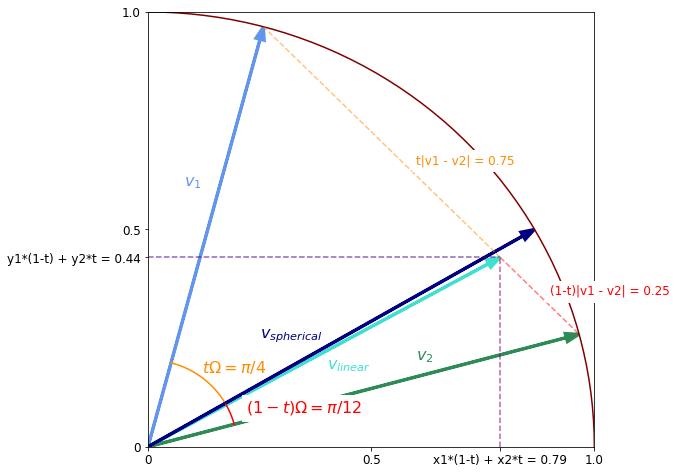
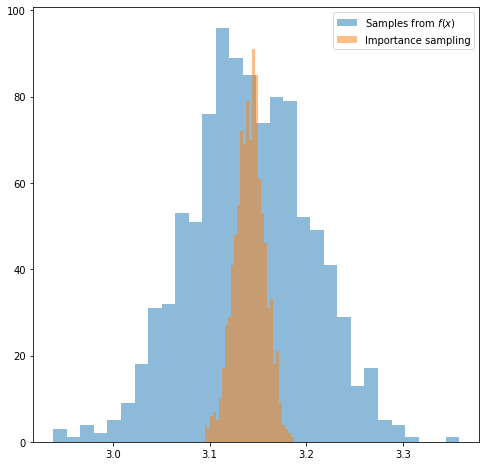
A Quick Introduction to Importance Sampling
You might have encountered the term importance sampling in a machine learning paper. This post provides a quick hands-on introduction to this topic. Hopefully after reading it you will have know understand how to use this technique in practice.
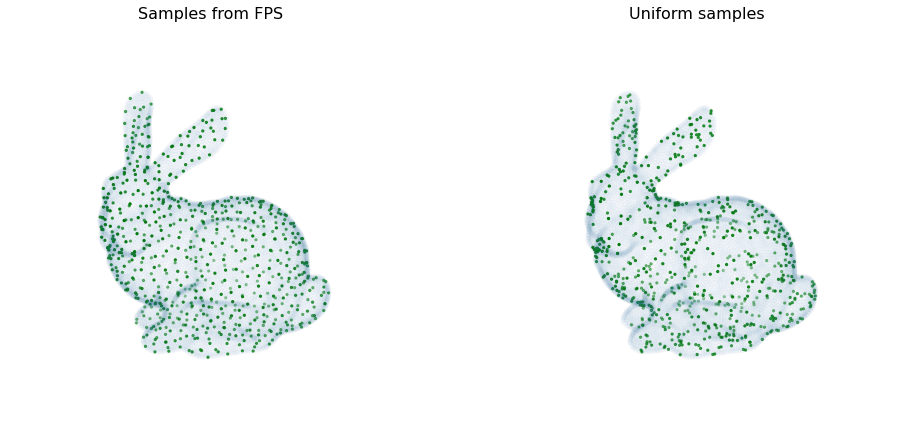
Furthest Point Sampling
I have come across an algorithm named furthest point sampling or sometimes farthest point sampling a few times in deep learning papers dealing with point cloud data. However there is a lack of resources online explaining what this algorithm actually does. Here I will try to explain it with reference to this CUDA implementation. Along the way we will also see how to implement it in an efficient parallelised way.
pytorch
A quick introduction to super-resolution using Stable Diffusion and the Diffusers library
In this blog post, we will show how to use the diffusers library to upscale images using the Stable Diffusion Upscaler model. The model is a diffusion-based super-resolution model that is capable of generating high-quality upscaled images.

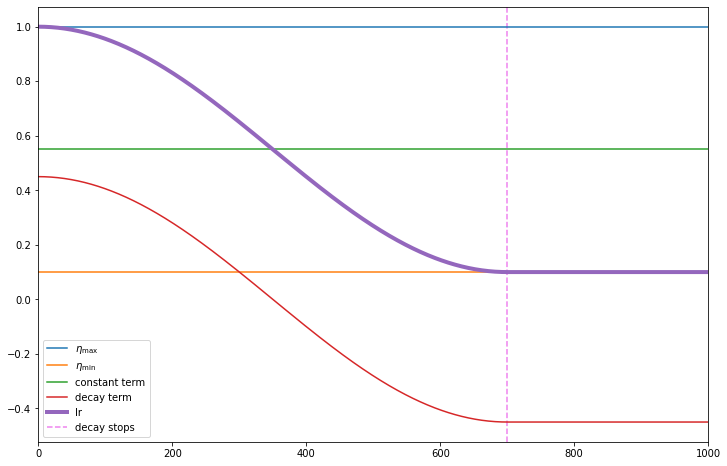
Cosine Learning Rate Decay
In this post we will introduce the key hyperparameters involved in cosine decay and take a look at how the decay part can be achieved in TensorFlow and PyTorch. In a subsequent blog we will look at how to add restarts.
Padding in PyTorch and TensorFlow embedding layers
When batching inputs for sequence models you often have sequences of variable sizes and you need to pad some of the inputs so that you can input them as a single tensor. For example here is a pair of lines in a dialogue from Twelfth Night Act 2, Scene 4 which are of variable length as represented here

However you don’t want the pad locations to influence the weight updates. In this post we will learn how PyTorch and TensorFlow approach this via their respective embedding layers.
tensorflow
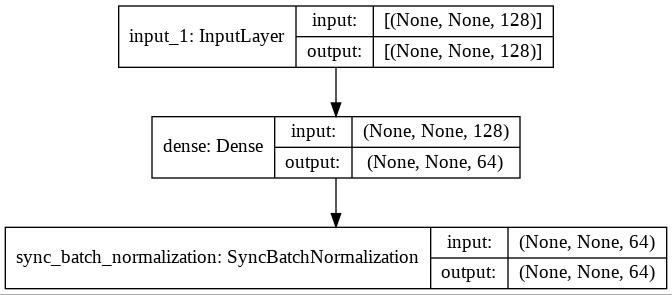
Distributed BatchNorm in TensorFlow
In this post we will see an example of how BatchNorm works when running distributed training with TensorFlow using TPUs and tf.keras.layers. This post assumes you know BatchNormalisation works.
Cosine Learning Rate Decay
In this post we will introduce the key hyperparameters involved in cosine decay and take a look at how the decay part can be achieved in TensorFlow and PyTorch. In a subsequent blog we will look at how to add restarts.

Padding in PyTorch and TensorFlow embedding layers
When batching inputs for sequence models you often have sequences of variable sizes and you need to pad some of the inputs so that you can input them as a single tensor. For example here is a pair of lines in a dialogue from Twelfth Night Act 2, Scene 4 which are of variable length as represented here

However you don’t want the pad locations to influence the weight updates. In this post we will learn how PyTorch and TensorFlow approach this via their respective embedding layers.
llm
A Minimalist ChatGPT for Jupyter Notebook or Command Line
In this blog post, we will explore how to implement a minimalist ChatGPT-style app in a Jupyter Notebook. The goal is to provide an understanding of the important concepts, components, and techniques required to create a chat app on top of a large language model (LLM), specifically OpenAI’s GPT.

How to stream ChatGPT responses from the OpenAI API
In this blog post we will learn how you can replicate this experience of the ChatGPT web application by streaming responses from the OpenAI API.

How to generate subtitles with the Whisper API in Python
In this tutorial we will learn how to use the Whisper API to generate subtitles for a video. We will generate subtitles for the opening of A Star Is Born (1937), an early colour movie that has been frequently remade.

optimization
Distributed BatchNorm in TensorFlow
In this post we will see an example of how BatchNorm works when running distributed training with TensorFlow using TPUs and tf.keras.layers. This post assumes you know BatchNormalisation works.

Cosine Learning Rate Decay
In this post we will introduce the key hyperparameters involved in cosine decay and take a look at how the decay part can be achieved in TensorFlow and PyTorch. In a subsequent blog we will look at how to add restarts.

metrics
Implementing the Fréchet Inception distance
A popular metric for evaluating image generation models is the Fréchet Inception Distance (FID). Like the Inception score, it is computed on the embeddings from an Inception model. But unlike the Inception score, it makes use of the true images as well as the generated ones. In the post we will learn how to implement it in PyTorch.

Vectorizing Intersection over Union (IoU)
Supporting batched data is an important requirement for a deep learning pipeline to enable time efficient model training. Often when writing a function, the easiest way to start is to first handle one element and then use a for loop over all the elements in the batch.

transformer
Transformer Part 2: Train a Translation Model
In Part 1 of the tutorial we learned how to how build a transformer model. Now it is time to put it into action. There are lots of things we can do with a transformer but we will start off with a machine translation task to translate from Spanish to English.

Transformer Part 1: Build
Since its introduction the Transformer architecture has become very influential and has had successes in many tasks not just in NLP but in other areas like vision. This tutorial is inspired by the approach in The Annotated Transformer and uses text directly quoted from the paper to explain the code.

attention
Transformer Part 2: Train a Translation Model
In Part 1 of the tutorial we learned how to how build a transformer model. Now it is time to put it into action. There are lots of things we can do with a transformer but we will start off with a machine translation task to translate from Spanish to English.

Transformer Part 1: Build
Since its introduction the Transformer architecture has become very influential and has had successes in many tasks not just in NLP but in other areas like vision. This tutorial is inspired by the approach in The Annotated Transformer and uses text directly quoted from the paper to explain the code.

visualisation
How to plot a Windrose in Python
A windrose is a circular histogram that shows the distribution of wind speeds and directions over a period of time. In this tutorial we will learn how to plot a windrose in Python using Matplotlib and Plotly.

Animations in Plotly.js
In this blog, we will demystify the process of creating interactive animations using Plotly.js.

augmentation
Generating crops from images
This post explains how to implement a function to generate a crop of a particular object from an image given the position of the centroid of the object. The images below show an example use case: cropping all the individual oranges from an image.

vae
Variational Auto-Encoder - Part 1 / Introduction
Consider this painting by Vincent Van Gogh known as “Wheatfield with Crows”. Suppose you want to learn a probability distribution over Van Gogh’s paintings. What the computer or a deep learning algorithm sees when it looks at this painting is a grid of RGB pixel intensities. So one approach might be to model the data as a sequence of individual pixels. Yet that is manifestly not how the artist has constructed the painting.

normalization
Distributed BatchNorm in TensorFlow
In this post we will see an example of how BatchNorm works when running distributed training with TensorFlow using TPUs and tf.keras.layers. This post assumes you know BatchNormalisation works.

algorithms
Strassen’s algorithm for matrix multiplication
This is the first of a planned series of blogs covering background topics for DeepMind’s AlphaTensor paper. In this post we will cover Strassen’s algorithm for matrix multiplication.

auto-regressive
PixelCNN
The PixelRNN family of auto-regressive architectures consists of models that learn to generate images a pixel at a time. In this post we will focus on the PixelCNN model which is based on the same principles but uses convolutional layers instead of recurrent layers. It is simpler to implement and once we have grasped the core concepts, it is straightforward to understand the recurrent versions.
speech
How to generate subtitles with the Whisper API in Python
In this tutorial we will learn how to use the Whisper API to generate subtitles for a video. We will generate subtitles for the opening of A Star Is Born (1937), an early colour movie that has been frequently remade.

segmentation
Turbulent flow segmentation with SAM
A simple example demonstrating the use of Meta’s Segment Anything Model (SAM) on a video of turbulent fluid flow.

quantum
How to Create Quantum Gate Diagrams in Python
A key concept in quantum computing is the quantum logic gate. Quantum gates are the building blocks of quantum circuits. In this blog we will learn how to create quantum gate and quantum circuit diagrams in Python using the SymPy library.

super-resolution
A quick introduction to super-resolution using Stable Diffusion and the Diffusers library
In this blog post, we will show how to use the diffusers library to upscale images using the Stable Diffusion Upscaler model. The model is a diffusion-based super-resolution model that is capable of generating high-quality upscaled images.
